http://annedavin.com/discovery/what-is-reality-therapy/
http://annedavin.com/discovery/what-is-reality-therapy/
Ways of Being:
Role of the counselor is to help the client take responsibility of their choices and to respect the client's quality world. The counselor offers a safe environment for the client to feel power and freedom and the relationship between counselor client provides the need of love and belonging. The counselor should be compassionate and empathetic towards the client, but do not place the main focus on the client's symptoms. The counselor it the teacher of choice theory.
Role of the client is to be authentic in sessions and to learn how to take responsibility for their own choices. The client becomes aware of their basic needs and total behavior. The client allows the counselor to enter into their quality world.
Role of the therapeutic relationship it is a positive and teaching relationship, that is focused in the present. The client learns the WDEP model to help realign their behavior and choices to satisfy their needs by helping the client to figure out exactly what they want.
Role of the counselor is to help the client take responsibility of their choices and to respect the client's quality world. The counselor offers a safe environment for the client to feel power and freedom and the relationship between counselor client provides the need of love and belonging. The counselor should be compassionate and empathetic towards the client, but do not place the main focus on the client's symptoms. The counselor it the teacher of choice theory.
Role of the client is to be authentic in sessions and to learn how to take responsibility for their own choices. The client becomes aware of their basic needs and total behavior. The client allows the counselor to enter into their quality world.
Role of the therapeutic relationship it is a positive and teaching relationship, that is focused in the present. The client learns the WDEP model to help realign their behavior and choices to satisfy their needs by helping the client to figure out exactly what they want.
 https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/originals/jpg
https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/originals/jpg
Ways of Understanding:
View of human nature is that people are internally motivated and can control their own behaviors. The external factors/environment provides people with information and people make decision from a conscious level. People are motivated to satisfy one or more of the five basic human needs; (1) Survival, humans are genetically wired for survival and are expressed through behaviors. (2) Love and belonging "is the primary human need. This is because we need other people in our lives to meet the rest of our needs" (Sommers-Flanagan, 304). (3) Power is a persons achievements and inner control. Power starts at early childhood with how one becomes to associate it. (4) Freedom or independence mainly thought of when its threaten. When one has limited freedom people get creative with solutions and symptoms. (5) Fun "the day we stop playing is the day we stop learning. It is the easiest need to satisfy" (Sommers-Flanagan, 308). This needs is usually blended with love and belonging.
Quality world is the person wants; (1) People, (2) Things or experiences or activities, (3) Ideas or system of belief. The wants in the quality world move in and out slowly. The counselor must understand and respect the clients quality world and through positive therapeutic relationship become apart of the clients. quality world.
Total behavior "includes four distinct, but inseparable, components that are always occurring simultaneously; (1) acting, (2) thinking, (3) feeling, (4) physiology" (Sommers-Flanagan, 309). The choice of how one chooses to act and think effects one's feeling and physiology directly.
View of the problem/ maladaptive behavior: William Glasser does not believe in mental illness not medication, but symptoms are cause by the choices that are made. (1) Restraining anger it is more "socially" acceptable to depress anger, so the client is depressing. (2) Getting help; helping the client evaluate if their symptoms are helping the client get their basic needs met and if there is a better choice to make. (3) Avoiding things; "depressing, panicking, obsessing, and many other behaviors commonly considered to be mental illness are excellent ways to avoid dealing with life situations that need to be addressed" (Sommers-Flanagan, 312).
View of healthy/ adaptive behavior: The client is able to meet their basic needs and are aligned with their quality world. The client is not trying to control or have power over others. Their behavior is to satisfy the needs effectively and easily.
Goals of theory: Is for clients to take responsibility of their choices and are able to meet their needs with a healthy behavior. Help the clients clarify their wants within their quality world and set realistic goals. The goal is to build the relationship with the client to become a part of their quality world and encourage behavior change.
Key concepts: The five basic human needs- survival, love and belonging, power, freedom, and fun.
Quality world- people, things/experiences/activities, and ideas/system of belief.
Total behavior- acting, thinking, feeling, and physiology.
Unhappiness comes from trying to the control others and the only person one can control is their self.
The focus is on one's choice and behaviors to satisfy one or more basic needs.
Glasser change the language to ending in ing, such as depressing, obsessing, to emphasize the client is actively making the choice.
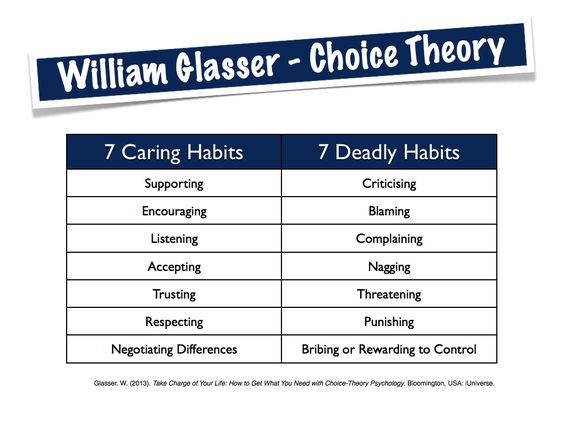
Seven caring habits: supporting, encouraging, listening, accepting, trusting, respecting, negotiating difference.
Seven deadly habits: criticizing, blaming, complaining, nagging, threatening, punishing, bribing or rewarding to control.
View of therapeutic change: Is the client able to easily make choices that will get their needs meet with healthy, adaptable behaviors. The client becomes aware one can only control their behavior and will not try to control others. The power dynamic shifts from trying to control others to self achievements. Also, the clients basic needs are being met and/or the client is aware of how to get their need met.
View of human nature is that people are internally motivated and can control their own behaviors. The external factors/environment provides people with information and people make decision from a conscious level. People are motivated to satisfy one or more of the five basic human needs; (1) Survival, humans are genetically wired for survival and are expressed through behaviors. (2) Love and belonging "is the primary human need. This is because we need other people in our lives to meet the rest of our needs" (Sommers-Flanagan, 304). (3) Power is a persons achievements and inner control. Power starts at early childhood with how one becomes to associate it. (4) Freedom or independence mainly thought of when its threaten. When one has limited freedom people get creative with solutions and symptoms. (5) Fun "the day we stop playing is the day we stop learning. It is the easiest need to satisfy" (Sommers-Flanagan, 308). This needs is usually blended with love and belonging.
Quality world is the person wants; (1) People, (2) Things or experiences or activities, (3) Ideas or system of belief. The wants in the quality world move in and out slowly. The counselor must understand and respect the clients quality world and through positive therapeutic relationship become apart of the clients. quality world.
Total behavior "includes four distinct, but inseparable, components that are always occurring simultaneously; (1) acting, (2) thinking, (3) feeling, (4) physiology" (Sommers-Flanagan, 309). The choice of how one chooses to act and think effects one's feeling and physiology directly.
View of the problem/ maladaptive behavior: William Glasser does not believe in mental illness not medication, but symptoms are cause by the choices that are made. (1) Restraining anger it is more "socially" acceptable to depress anger, so the client is depressing. (2) Getting help; helping the client evaluate if their symptoms are helping the client get their basic needs met and if there is a better choice to make. (3) Avoiding things; "depressing, panicking, obsessing, and many other behaviors commonly considered to be mental illness are excellent ways to avoid dealing with life situations that need to be addressed" (Sommers-Flanagan, 312).
View of healthy/ adaptive behavior: The client is able to meet their basic needs and are aligned with their quality world. The client is not trying to control or have power over others. Their behavior is to satisfy the needs effectively and easily.
Goals of theory: Is for clients to take responsibility of their choices and are able to meet their needs with a healthy behavior. Help the clients clarify their wants within their quality world and set realistic goals. The goal is to build the relationship with the client to become a part of their quality world and encourage behavior change.
Key concepts: The five basic human needs- survival, love and belonging, power, freedom, and fun.
Quality world- people, things/experiences/activities, and ideas/system of belief.
Total behavior- acting, thinking, feeling, and physiology.
Unhappiness comes from trying to the control others and the only person one can control is their self.
The focus is on one's choice and behaviors to satisfy one or more basic needs.
Glasser change the language to ending in ing, such as depressing, obsessing, to emphasize the client is actively making the choice.
Seven caring habits: supporting, encouraging, listening, accepting, trusting, respecting, negotiating difference.
Seven deadly habits: criticizing, blaming, complaining, nagging, threatening, punishing, bribing or rewarding to control.
View of therapeutic change: Is the client able to easily make choices that will get their needs meet with healthy, adaptable behaviors. The client becomes aware one can only control their behavior and will not try to control others. The power dynamic shifts from trying to control others to self achievements. Also, the clients basic needs are being met and/or the client is aware of how to get their need met.
Ways of Intervening:
Techniques: Counselors do not use standardized assessments, but use interviewing, while the counselor is interview they are evaluating to answer what does the client want, what is the client doing, is it working, and should the client make a new plan?. Building a relationship with the client using the seven caring habits: (1) supporting, (2) encouraging, (3) listening, (4) accepting, (5) trusting, (6) respecting, and (7) negotiating differences, this brings awareness of choice. Developing an effective plan by using SAMIC^3: S=simple, keep it clear and concert, A=attainable, keep the goals attainable and realistic, M=measurable, what do the goals look like, I=immediate, implement plan immediately, C=controlled, are based within the clients control, C=committed, client needs to be committed to their plan, C=continuous, the plan is continuous implementing.
Multicultural considerations: This theory is not culturally specific, but has been used more in western therapy. The theory can be modified to working with different cultural backgrounds. This therapy can be empowering, but does not take external factors or social power in consideration.
Working with groups: This therapy would work well in group therapy sessions because clients are able to see how their choice effect them and relate to other members.
Limitations: Choice theory/reality therapy does have sufficient evidence based research main in school settings. The therapy "does not rely on formal assessment procedures" (Sommers-Flanagan, 330). Glasser does not believe in mental illness or medication, which could be limiting to clients with a brain imbalance.
Techniques: Counselors do not use standardized assessments, but use interviewing, while the counselor is interview they are evaluating to answer what does the client want, what is the client doing, is it working, and should the client make a new plan?. Building a relationship with the client using the seven caring habits: (1) supporting, (2) encouraging, (3) listening, (4) accepting, (5) trusting, (6) respecting, and (7) negotiating differences, this brings awareness of choice. Developing an effective plan by using SAMIC^3: S=simple, keep it clear and concert, A=attainable, keep the goals attainable and realistic, M=measurable, what do the goals look like, I=immediate, implement plan immediately, C=controlled, are based within the clients control, C=committed, client needs to be committed to their plan, C=continuous, the plan is continuous implementing.
Multicultural considerations: This theory is not culturally specific, but has been used more in western therapy. The theory can be modified to working with different cultural backgrounds. This therapy can be empowering, but does not take external factors or social power in consideration.
Working with groups: This therapy would work well in group therapy sessions because clients are able to see how their choice effect them and relate to other members.
Limitations: Choice theory/reality therapy does have sufficient evidence based research main in school settings. The therapy "does not rely on formal assessment procedures" (Sommers-Flanagan, 330). Glasser does not believe in mental illness or medication, which could be limiting to clients with a brain imbalance.